Introduction
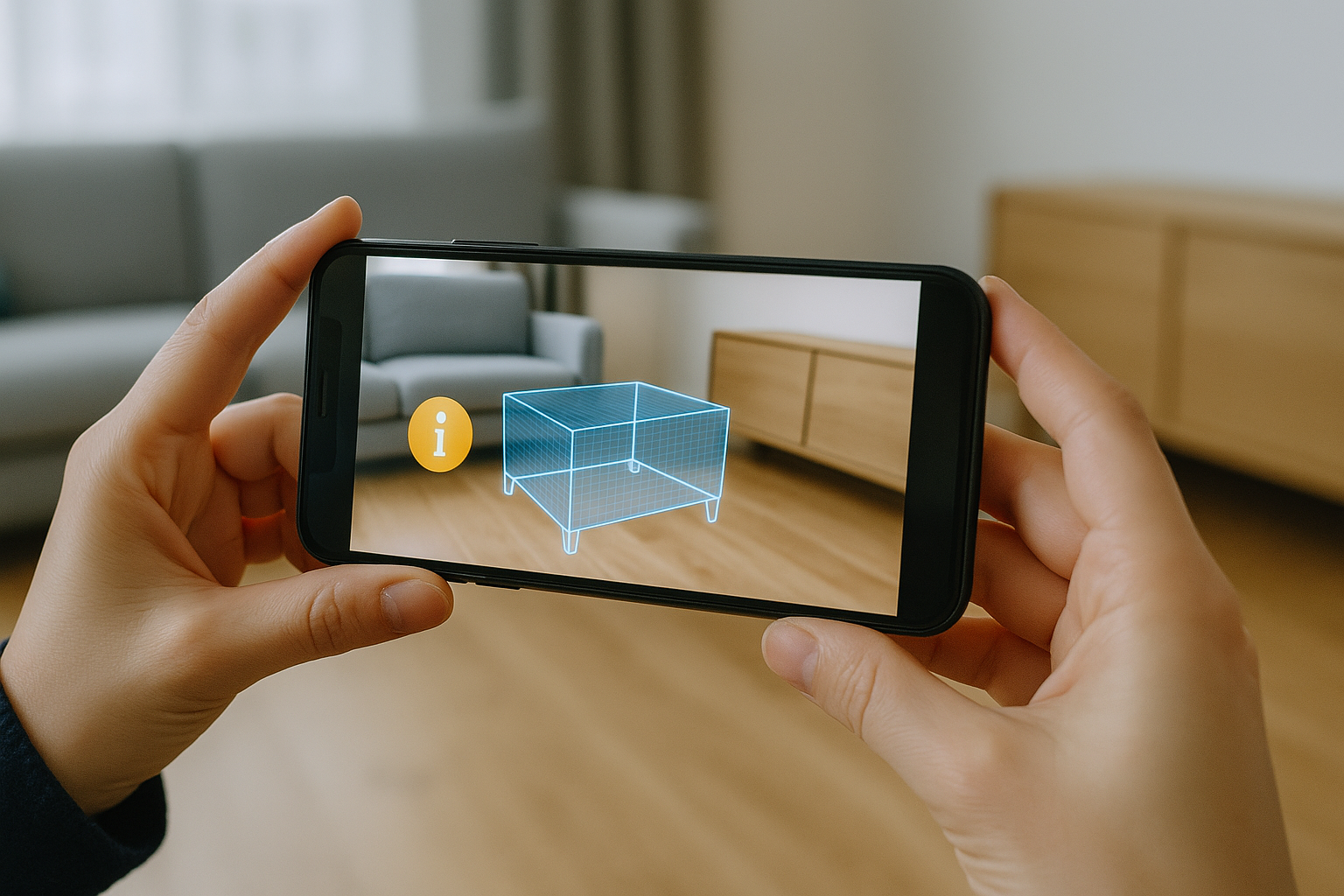
Imagine walking through a city while holding up your smartphone, and instead of only seeing buildings and streets, your screen displays restaurant ratings, historic facts about the monuments, or even virtual characters playing in front of you. This isn’t science fiction — it’s Augmented Reality, or AR.
AR is already integrated into our everyday lives, often without us even realizing it. Whether you’re using a filter on Instagram, scanning a QR code that opens a 3D model, or playing Pokémon Go, you’ve already interacted with this technology.
But AR goes far beyond social media filters and games. It’s influencing how we shop, learn, work, heal, travel, and create. In this article, we’ll explore what AR is, how it works, where it’s used, and why it’s becoming one of the most significant technological trends of our time.
What Is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes digital content over the real world, in real time. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR) — which immerses you in a completely artificial environment — AR enhances your current environment without removing you from it.
AR uses a combination of hardware (such as a smartphone or AR glasses), sensors (to detect movement and orientation), and software (to interpret data and place digital objects). The result is a seamless blend of physical and digital experiences that feel interactive, intuitive, and personal.
For example, AR can place a virtual couch in your living room before you buy it, show live directions on the road while you drive, or help a surgeon visualize internal organs without making an incision.
How Does AR Work?
AR relies on several key technologies:
- Cameras and Sensors: To scan and understand the physical environment
- Processors: To analyze the data and generate digital overlays
- Displays: To show digital content through phones, tablets, smart glasses, or AR headsets
- Software: To map the environment, place virtual elements, and allow interaction
Modern AR uses advanced algorithms such as:
- SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping): Builds a real-time map of your environment to anchor digital objects
- Depth Tracking: Measures distances between the camera and objects
- Plane Detection: Identifies flat surfaces like floors and tables
- Image Recognition: Identifies objects or markers to trigger AR effects
These components work together to create dynamic, location-aware, and interactive digital experiences that can respond to your movements and surroundings.
Everyday Uses of Augmented Reality
Many people have already used AR — often without realizing it. Here are just a few examples:
- Social Media Filters: Snapchat, Instagram, and TikTok filters that alter your face or surroundings
- Retail Apps: Apps that let you try on makeup, clothes, or glasses virtually
- Home Design Tools: Visualizing how furniture will look in your space
- Navigation Apps: Google Maps’ Live View shows arrows and directions over real-world streets
- Games: Pokémon Go, Harry Potter: Wizards Unite, and other location-based games
These experiences are fun, engaging, and easy to access — usually through a smartphone camera.
Where Is Augmented Reality Used?
1. Retail and E-Commerce
AR is transforming how people shop — online and in physical stores. Brands are using AR to create more personalized, confident, and satisfying customer experiences.
Examples:
- Virtual Try-On: L’Oréal and Sephora offer virtual makeup tools. Warby Parker lets you try glasses virtually.
- Preview Before Purchase: IKEA Place shows how furniture will fit in your room.
- Interactive Packaging: Scanning a product can unlock animations, games, or instructions.
Customers can see how products look, feel, and function — without needing to touch them. This reduces returns and improves sales conversion.
2. Education and Learning
AR is helping students understand complex topics through interactive, visual experiences.
Examples:
- 3D Biology Models: Apps like Froggipedia let students dissect frogs virtually.
- History Lessons: Bringing historical events or ancient architecture to life in the classroom.
- Language Learning: Real-time translation and contextual visual cues make learning more immersive.
Teachers can use AR to create hands-on learning environments without expensive labs or materials. It’s especially effective in STEM education, medical training, and early childhood development.
3. Healthcare
AR is playing a critical role in enhancing medical procedures and training.
Examples:
- Surgical Assistance: AR headsets help doctors visualize organs and blood vessels during operations.
- Physical Therapy: Patients follow AR-based exercises, improving motivation and progress tracking.
- Medical Training: Students can practice complex procedures in a risk-free virtual space.
Hospitals also use AR to explain diagnoses to patients, improving communication and reducing anxiety.
4. Manufacturing and Maintenance
In factories and workshops, AR helps workers perform tasks faster, more accurately, and with less training.
Examples:
- Assembly Guides: AR displays step-by-step instructions over machinery or components.
- Remote Support: A technician can assist another worker from anywhere by seeing what they see through AR glasses.
- Quality Control: Visual indicators help identify errors or misalignments in real time.
Companies like Boeing and Ford use AR to improve productivity and reduce errors on the production floor.
5. Architecture and Real Estate
AR lets architects, designers, and buyers experience spaces before they are built.
Examples:
- Virtual Tours: Walk through a building while it’s still under construction.
- Interior Design: See how paint colors, furniture, or layout changes will look.
- Blueprint Overlay: Contractors can view plans directly over physical construction sites.
Buyers and clients make decisions faster and with more confidence when they can see what the final result will look like.
6. Automotive and Navigation
AR is enhancing the driving experience by making navigation safer and more intuitive.
Examples:
- Heads-Up Displays (HUDs): Project speed, directions, and warnings onto the windshield.
- AR Dashboards: Show road conditions or hazard alerts in real time.
- Maintenance: Step-by-step repair guides for car owners and mechanics.
AR helps reduce distractions by keeping drivers focused on the road while still accessing necessary information.
7. Tourism and Culture
AR allows tourists and visitors to engage more deeply with places, cultures, and history.
Examples:
- Historical Overlays: See how ruins looked in their prime.
- Museum Exhibits: Trigger animations or explanations by scanning an artifact.
- Language Translation: Instantly understand signs or menus abroad.
Cities and cultural institutions are using AR to create smart tourism experiences that are both educational and fun.
AR for Accessibility and Inclusion
AR isn’t just for entertainment or business — it’s also improving quality of life for people with disabilities.
Examples:
- Visual Assistance: Apps like Envision AI read text aloud and describe objects for blind users.
- Subtitling and Sign Language: Real-time translation for the deaf or hard-of-hearing.
- Cognitive Support: AR routines and cues for people with autism or memory challenges.
By adapting content to individual needs, AR fosters greater independence and participation.
AR in Marketing and Branding
Brands are using AR to create memorable and shareable experiences.
Examples:
- AR Filters: Branded lenses on Instagram or TikTok.
- Interactive Ads: Scan a magazine ad and watch it come to life.
- Gamified Campaigns: Scavenger hunts or virtual prizes tied to physical locations.
AR allows brands to build deeper engagement, especially with younger, tech-savvy audiences.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality
AR is evolving fast. Here’s what’s coming next:
- AR Glasses: Companies like Apple, Meta, and Google are investing heavily in wearable AR.
- WebAR: AR experiences directly in your browser — no app needed.
- AI + AR: Artificial intelligence will power smarter, more adaptive AR interactions.
- Persistent AR: Digital content that stays fixed in the same location for all users (e.g., AR graffiti or menus).
As 5G and edge computing become more widespread, AR experiences will become faster, smoother, and more immersive.
Challenges of AR
Despite its potential, AR faces some limitations:
- Battery Drain: Mobile AR can quickly exhaust devices.
- Privacy: Constant data collection raises concerns.
- Development Costs: Creating quality AR content requires time and expertise.
- User Comfort: Some people experience discomfort or motion sickness.
- Device Dependency: Widespread use still depends on smartphones or future AR wearables.
However, as technology improves and becomes more affordable, these challenges are being addressed.
Getting Started with AR
You don’t need to be a tech expert to explore AR.
Here’s how anyone can start:
- Use free apps: Try IKEA Place, Google Lens, or Snapchat filters.
- Learn AR creation tools: Platforms like Spark AR, Unity, and 8thWall let you build your own AR experiences.
- Stay updated: Follow AR news, blogs, and creators to see what’s possible.
Whether you’re a business owner, content creator, teacher, or simply curious, AR offers tools that can bring your ideas to life.
Final Thoughts
Augmented Reality is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s a practical, powerful tool that’s shaping how we live, learn, shop, and connect.
From medical surgeries to online shopping, from classrooms to car dashboards, AR is transforming industries and unlocking new possibilities every day.
As AR becomes more accessible, businesses, educators, and everyday users have a unique opportunity: to not just consume digital experiences, but to create them.
The future isn’t just digital. It’s augmented — and it’s already here.