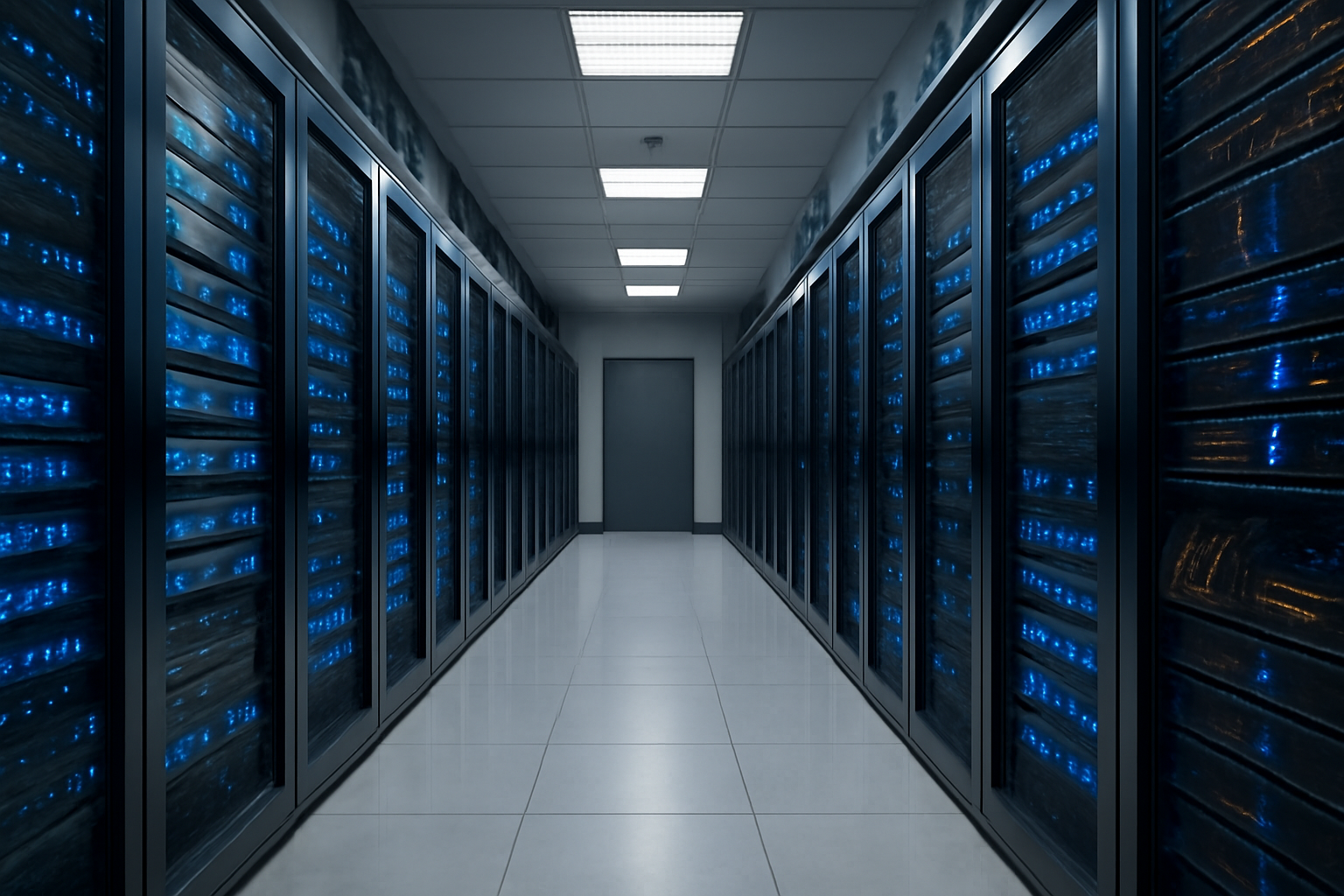
In today’s digital world, data is the lifeblood of virtually every industry, powering everything from social media and e-commerce to financial transactions and cloud services. As our reliance on digital systems grows, so too does the need to store, manage, and protect data efficiently and securely. This is where data centers come into play.
Data centers are the backbone of the digital economy, providing the infrastructure necessary to store and process data. They are responsible for keeping the digital world running smoothly, ensuring that information is accessible, secure, and available whenever it’s needed. But what exactly is a data center, and why is it so important in our increasingly connected world? In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of data centers, how they work, and their significance in today’s tech-driven landscape.
1. Understanding Data Centers: The Basics
What Is a Data Center?
A data center is a facility that houses a large number of physical servers, network equipment, and other hardware used to store, manage, and process vast amounts of data. These facilities are designed to ensure that digital services and applications, from cloud storage to web hosting, function reliably and securely.
Data centers are equipped with specialized infrastructure to support the operation of servers and other hardware. This includes high-capacity cooling systems, backup power supplies, and robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access. In simple terms, a data center is like a digital warehouse where all the information that powers the internet and businesses is stored, maintained, and made accessible to users across the globe.
Types of Data Centers
There are several types of data centers, each designed to meet different operational needs:
- Enterprise Data Centers: These are owned and operated by large companies to support their internal operations. They are typically located on-premises and are used to manage the company’s own data and IT infrastructure.
- Colocation Data Centers: In these facilities, companies rent space to house their servers and other hardware. The data center operator manages the infrastructure, but the company maintains control over its equipment and data.
- Cloud Data Centers: Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure operate massive data centers that host and manage data for customers. These centers are part of the cloud computing infrastructure, where businesses and individuals can store data and run applications without having to maintain physical hardware.
2. How Do Data Centers Work?
The Role of Servers and Storage
At the heart of every data center are servers – powerful computers designed to process and store data. These servers run applications, manage websites, and provide cloud-based services. Servers in a data center are typically organized in racks, allowing for efficient use of space while ensuring proper ventilation and cooling.
Storage is another crucial component of a data center. It refers to the systems that hold vast amounts of data, from documents and images to videos and software. Modern data centers often use high-performance storage solutions, such as Solid-State Drives (SSDs) or hard disk arrays, to ensure fast and reliable access to data.
Networking and Connectivity
In addition to servers and storage, data centers require robust networking infrastructure. Data centers are connected to the internet via high-speed fiber optic cables, ensuring rapid data transfer between servers and users across the world. The networking equipment inside a data center – including routers, switches, and firewalls – enables seamless communication and ensures that data flows securely between the facility and its users.
Networking in data centers is designed to minimize downtime and ensure redundancy. If one component fails, there are backups in place to ensure continuous service. This level of reliability is crucial for businesses that depend on constant access to data, such as e-commerce sites, financial institutions, and healthcare providers.
Cooling and Power Systems
Data centers generate a significant amount of heat due to the constant operation of servers and other equipment. To maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating, data centers are equipped with advanced cooling systems, such as air conditioning units, liquid cooling systems, and even geothermal cooling techniques.
Power management is also essential. Data centers typically have multiple power sources, including backup generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), to ensure that operations continue without disruption during power outages. This level of redundancy is critical to avoid downtime, which could be costly for businesses and their customers.
3. Why Are Data Centers So Important?
The Backbone of Cloud Computing
One of the primary reasons data centers are so important is their role in cloud computing. The vast majority of cloud-based services rely on data centers to store and process information. Whether you’re using Google Drive, Netflix, or an online banking app, the data that powers these services is stored in data centers.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access data and services, eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and providing the flexibility to scale resources as needed. Data centers make this possible by providing the infrastructure that supports cloud providers and ensures that services remain fast, reliable, and secure.
Ensuring Data Security
Data centers also play a vital role in data security. With the increasing amount of sensitive data being stored online, it is crucial to protect that data from cyber threats, including hacking, malware, and data breaches.
To prevent unauthorized access, data centers are equipped with advanced security systems, such as biometric access controls, surveillance cameras, and firewalls. Many data centers also employ physical security measures, including guards and fencing, to protect the hardware from theft or damage. Furthermore, data centers comply with industry regulations and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data.
Supporting Business Operations
For businesses, data centers are essential for ensuring continuity and minimizing downtime. Businesses depend on data centers to host their websites, store customer information, run applications, and process transactions. A well-managed data center can help ensure that these operations run smoothly, with minimal risk of disruptions.
In addition, businesses that operate in multiple regions often rely on data centers in different locations to provide redundancy and ensure that their services remain available even if one data center experiences an issue. This level of reliability and uptime is crucial for businesses that serve global customers.
Enabling Innovation and Digital Transformation
Data centers are the driving force behind digital transformation. As businesses adopt new technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, the need for powerful and scalable data storage and processing increases. Data centers provide the infrastructure necessary to support these technologies, allowing businesses to innovate and stay competitive.
For example, AI models require vast amounts of data to train and operate. Data centers provide the storage and computational power needed to process this data quickly and efficiently. Similarly, IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, which must be stored and analyzed in real time. Data centers enable this by providing the necessary computing resources and network connectivity.
4. The Future of Data Centers
Green Data Centers
As concerns about climate change and energy consumption grow, the focus on sustainable data centers is becoming more important. Green data centers are designed to reduce their environmental impact by using energy-efficient technologies, such as renewable energy sources (solar, wind), advanced cooling techniques, and efficient power management systems.
Many companies are now committed to operating carbon-neutral data centers, ensuring that their operations do not contribute to global warming. This shift towards sustainability is not only good for the environment but also helps businesses reduce operating costs in the long term.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Data Centers
Another trend in the future of data centers is the rise of edge computing. As the demand for faster data processing and lower latency increases, more data centers are being located closer to end users. Edge data centers are smaller facilities that are located at the “edge” of the network, closer to where data is generated and consumed. This helps reduce latency and enables faster response times, making it ideal for applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and real-time analytics.
Edge computing is expected to grow significantly in the coming years as more industries require faster processing speeds and increased connectivity. This trend will drive the demand for decentralized data centers that can process data more locally, reducing reliance on large, centralized facilities.
5. Conclusion
Data centers are the hidden infrastructure that powers our digital lives. From cloud computing and data storage to ensuring data security and enabling innovation, they play an essential role in today’s tech-driven world. As the demand for digital services continues to grow, so too does the importance of data centers in maintaining the reliability, security, and scalability of these services.
With advancements in technology, such as green data centers and edge computing, the future of data centers looks promising. They will continue to evolve, becoming more sustainable, efficient, and decentralized, ensuring that businesses and consumers alike can benefit from fast, secure, and reliable access to digital services.