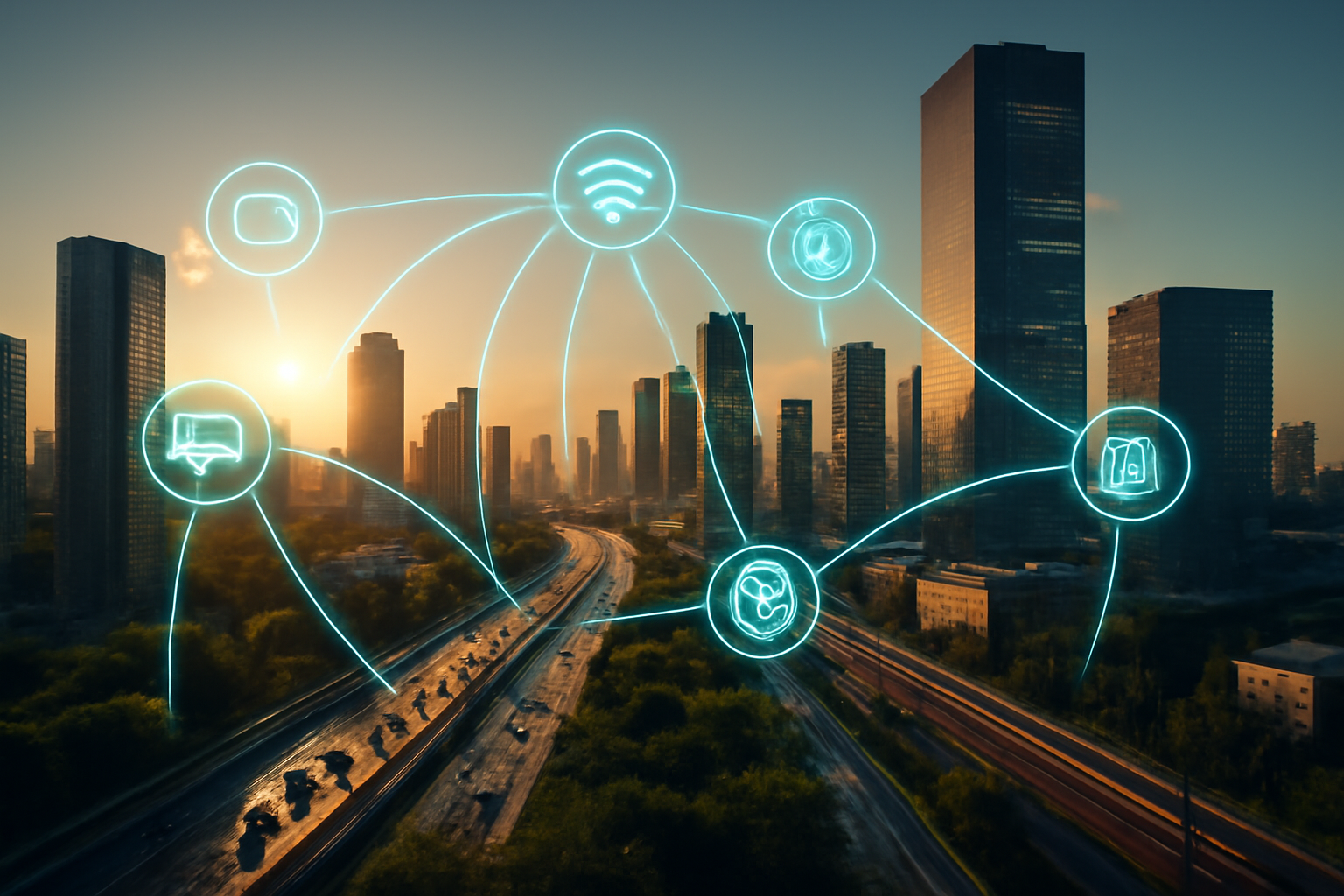
The concept of smart cities has become a central topic in discussions about the future of urban living. As cities continue to grow and the challenges of urbanization become more complex, the integration of technology into urban planning and infrastructure has the potential to revolutionize how we live, work, and interact with our environment. But what exactly are smart cities, and how do they function in practice?
In this article, we’ll explore the definition of smart cities, the technologies that power them, the benefits and challenges they bring, and how they are reshaping urban landscapes for a more sustainable, efficient, and livable future.
1. Defining Smart Cities
What Makes a City “Smart”?
A smart city is one that uses digital technologies, data, and connectivity to enhance the quality of life for its residents, optimize resource usage, and ensure sustainability. These cities are designed to improve the efficiency of services, reduce environmental impact, and provide real-time information that helps both citizens and local governments make informed decisions.
Smart cities are built on the foundation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and data networks that collect vast amounts of information about everything from traffic patterns to air quality, energy consumption, and waste management. By analyzing this data, urban planners and local governments can make more effective decisions that improve the daily lives of their inhabitants.
The Core Components of Smart Cities
The key components that define a smart city typically include:
- Connectivity: A smart city is equipped with advanced broadband and wireless networks that allow for the seamless transfer of data across the city.
- Sensors and IoT: Sensors are embedded in various infrastructure, such as traffic lights, streetlights, buildings, and transportation systems. These sensors collect real-time data and send it to a central system for analysis.
- Big Data and Analytics: The vast amounts of data collected by IoT devices are processed using advanced analytics and machine learning to derive actionable insights.
- Automation: Many smart city functions, such as traffic management and energy use, are automated to reduce human intervention and improve efficiency.
- Sustainability: Smart cities prioritize environmental sustainability, integrating green technologies and solutions like renewable energy sources and waste recycling systems.
2. How Smart Cities Work: Key Technologies
The Role of IoT in Smart Cities
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the backbone of a smart city. IoT refers to a network of physical objects—such as vehicles, streetlights, buildings, and sensors—that are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other. These devices continuously send and receive data, enabling cities to monitor and manage resources efficiently.
For example, in a smart city, IoT sensors can monitor traffic flow, detect congestion, and adjust traffic lights in real time to improve vehicle flow. Similarly, IoT-enabled streetlights can automatically adjust brightness based on time of day or weather conditions, saving energy and reducing costs.
The ability to gather and analyze data from various IoT devices helps cities make better decisions, such as optimizing waste collection routes or predicting when maintenance is needed on public infrastructure.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Smart cities rely heavily on data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to process the vast amounts of information collected from IoT devices. With advanced algorithms, AI systems can identify patterns, make predictions, and provide insights that help cities operate more efficiently.
For example, AI can be used to predict traffic congestion patterns and suggest alternative routes for drivers. It can also help with predictive maintenance, where AI analyzes sensor data to forecast when infrastructure like roads, bridges, or public transport systems will need repair, preventing costly breakdowns and delays.
AI-powered systems can also enhance public safety. For instance, surveillance cameras equipped with AI can detect unusual behavior, such as large gatherings or suspicious activity, and alert authorities in real time, helping improve security in urban areas.
Smart Energy and Sustainability
One of the most significant aspects of smart cities is their emphasis on sustainability. With growing concerns over climate change, smart cities aim to reduce their environmental impact by optimizing energy use, promoting renewable energy sources, and reducing waste.
Smart grids are an excellent example of how smart cities integrate technology for energy management. These grids use IoT sensors and data analytics to monitor and control energy distribution in real time. This allows for more efficient energy use, reduces waste, and can even help cities integrate renewable energy sources like solar or wind power into the grid.
Additionally, smart waste management systems can improve the collection and recycling of waste. Sensors in waste bins can alert municipal authorities when they are full, ensuring that collection routes are optimized to reduce fuel consumption and labor costs. Smart cities can also use waste-to-energy technologies to turn waste into usable energy, creating a more sustainable waste management system.
3. Benefits of Smart Cities
Improved Quality of Life
Smart cities have the potential to drastically improve the quality of life for their residents. Real-time data and improved infrastructure can make cities more comfortable, efficient, and livable. For example, smart public transportation systems can provide accurate arrival times for buses and trains, reducing wait times and making commuting more predictable and less stressful.
Additionally, the integration of smart healthcare systems can improve medical services. IoT-enabled devices, such as wearable health trackers, can monitor individuals’ health and send real-time data to doctors or hospitals. This enables faster diagnosis and more personalized treatment, improving the overall healthcare experience for city residents.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings
Smart cities are designed to be more efficient by automating processes and using data to optimize operations. Automated systems can reduce the need for human intervention, lowering labor costs and minimizing human error. For instance, smart traffic management systems can reduce congestion and travel time, saving both time and fuel.
Moreover, smart cities often use predictive maintenance to prevent infrastructure failures. By identifying potential issues before they become major problems, cities can save money on repairs and improve the lifespan of infrastructure.
Environmental Sustainability
As mentioned earlier, sustainability is a critical focus of smart cities. The integration of green technologies and solutions helps reduce carbon footprints, lower energy consumption, and minimize waste. For example, energy-efficient buildings and renewable energy sources can help reduce a city’s reliance on fossil fuels, leading to cleaner air and a smaller environmental impact.
Smart cities also use data to monitor environmental conditions, such as air quality and water usage, allowing governments to take immediate action to mitigate pollution or waste. By promoting sustainable practices, smart cities aim to create a healthier and more eco-friendly environment for future generations.
4. Challenges of Smart Cities
Data Privacy and Security
While smart cities offer numerous benefits, they also present significant challenges, particularly around data privacy and security. As cities collect vast amounts of data through IoT devices and sensors, there is a growing concern about how this data is stored, used, and protected.
Smart cities need to implement robust cybersecurity measures to prevent hacking and protect citizens’ personal information. Additionally, clear data privacy regulations must be established to ensure that residents’ data is used ethically and responsibly.
Cost and Infrastructure
Building a smart city is a significant financial investment. The cost of implementing IoT devices, installing sensors, upgrading infrastructure, and developing data centers can be prohibitively high for many cities. This often requires public-private partnerships and large-scale funding from both government and private entities.
Furthermore, transitioning an existing city into a smart city requires significant upgrades to its infrastructure. This can involve retrofitting old buildings, replacing outdated systems, and creating new networks, all of which take time and resources.
Technological Integration and Interoperability
For smart cities to function effectively, different technologies and systems must work together seamlessly. However, many cities face challenges when it comes to integrating new technologies with older systems. Additionally, ensuring interoperability between different technologies, platforms, and devices is essential for the smooth operation of a smart city.
To address these issues, cities must establish clear standards and protocols for technology integration, ensuring that all systems can communicate and share data effectively.
5. The Future of Smart Cities
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the concept of smart cities. We are likely to see further advancements in AI, IoT, and data analytics that will enable even more sophisticated smart city solutions. The integration of emerging technologies such as 5G networks and blockchain will further enhance the capabilities of smart cities, improving efficiency, security, and transparency.
The future of smart cities also includes greater citizen participation. With the advent of technologies like blockchain, residents will have more control over their data and can participate in decision-making processes, ensuring that smart cities are developed in ways that truly meet the needs of their inhabitants.
Conclusion
Smart cities represent the future of urban living, where technology is harnessed to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments. By integrating IoT devices, AI, big data, and renewable energy solutions, cities can optimize resource usage, improve quality of life, and reduce their environmental impact. However, the development of smart cities also comes with challenges related to data security, infrastructure costs, and technological integration.
As we look ahead, smart cities will continue to evolve, driven by innovation and the need to address the growing challenges of urbanization. The cities of tomorrow will not only be smarter but also more inclusive, sustainable, and resilient, paving the way for a better urban experience for all.