Introduction: The Tap That Changed Everything
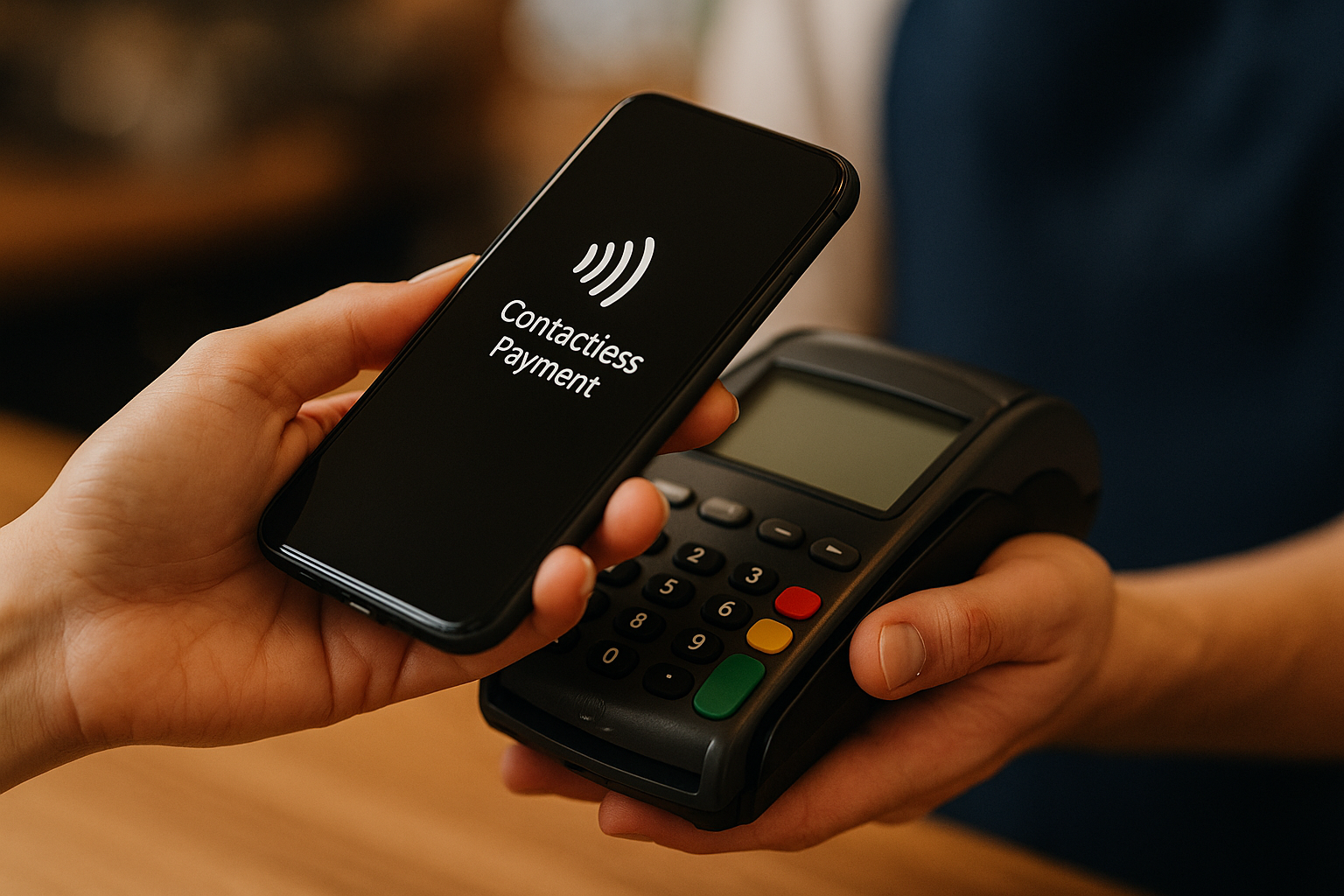
You’re at a coffee shop, you grab your favorite drink, and with a simple tap of your phone or card, the payment is complete—no cash, no PIN, no signature. This is the magic of contactless payments, a technology that’s quickly becoming the default choice for millions around the world. But how does this seamless, almost invisible process actually work?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the mechanics behind contactless payments, the technologies that power them, the security protocols in place, and their real-world impact. Whether you’re a tech-savvy professional or someone just curious about how these systems operate, you’ll find this guide both informative and engaging.
What Are Contactless Payments?
Contactless payments refer to transactions made without physical contact between a payment device (such as a card or mobile phone) and a point-of-sale terminal. Instead of swiping or inserting a card into a machine, you simply hold your device near a terminal equipped with the appropriate technology.
Common Methods of Contactless Payments:
- NFC-Enabled Credit or Debit Cards
- Mobile Wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay
- Wearables like smartwatches and fitness bands
- Contactless-Enabled Key Fobs or Tags
These payment solutions are often backed by major financial institutions and integrated with loyalty programs, transit systems, and biometric security, creating an interconnected ecosystem that offers both convenience and control to consumers.
The Technology Behind Contactless Payments
Near Field Communication (NFC)
The core technology that enables contactless payments is NFC—a subset of radio-frequency identification (RFID). NFC allows two electronic devices to exchange information over a distance of about 4 centimeters (1.6 inches).
The communication happens through electromagnetic fields:
- The POS terminal emits a signal.
- When your card or device is within range, it responds by transmitting the payment information.
- The terminal then processes this data and completes the transaction.
NFC chips are embedded in both the card and terminal and only activate in close proximity, ensuring that the payment is deliberate and secure.
EMV Chip Integration
Most contactless cards come embedded with EMV chips (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa), which provide cryptographic security features. These chips generate a one-time code for each transaction, making it nearly impossible to replicate or skim.
EMV chip-enabled contactless payments are recognized for enhancing data protection, providing dynamic transaction authentication, and deterring counterfeit fraud.
Step-by-Step: How a Contactless Payment Works
Let’s break down a typical contactless transaction:
- Initiation: The customer taps or holds their device/card near the POS terminal.
- Authentication: The terminal verifies that the card or device is NFC-enabled.
- Data Exchange: Encrypted payment data is transmitted from the card/device to the terminal.
- Tokenization: A one-time-use token replaces your actual card details, enhancing security.
- Authorization: The merchant’s bank sends the token to the card issuer for approval.
- Response: The issuer either approves or denies the transaction.
- Completion: If approved, the transaction is finalized and a receipt is printed or displayed.
This all happens in a matter of seconds, making contactless payments one of the fastest payment methods available today. The entire process is designed to be frictionless, user-friendly, and robust.
Security Measures and Misconceptions
Tokenization
One of the most important features of contactless payments is tokenization. Instead of transmitting your actual card number, the system uses a unique token that is valid for only one transaction.
This prevents fraudsters from using intercepted data for future purchases.
Encryption
The data transmitted is encrypted, reducing the risk of interception by third parties.
Limited Range
Because NFC works at very short distances, it’s unlikely that someone could intercept your transaction unless they are extremely close—usually within a couple of inches.
Spending Limits
Many banks set a limit on contactless transactions without PINs, often around $50 or equivalent. This limits potential losses if your card is lost or stolen.
Real-Time Monitoring
Financial institutions often monitor contactless transactions in real time, using AI to detect suspicious behavior. Users are typically notified immediately via mobile app or SMS in case of anomalies.
Misconceptions:
- “People can steal my info just by walking past.” Not really. NFC requires extremely close proximity and encryption adds another layer of protection.
- “Contactless is less secure than chip-and-PIN.” In reality, it’s just as secure—sometimes more—thanks to tokenization.
- “Contactless payments drain your battery.” Mobile payments do use some power, but it’s minimal compared to other app functions.
Benefits of Contactless Payments
Speed and Convenience
Transactions are completed in seconds, reducing wait times in stores, public transportation, and cafes.
Hygiene
Contactless payments became especially popular during the COVID-19 pandemic because they reduce physical contact with surfaces.
Versatility
You can use a card, phone, watch, or even your keychain to pay—no need to carry a wallet.
Travel-Friendly
Widely accepted globally, contactless payments are great for tourists. You can pay for trains, buses, or meals with the same ease anywhere NFC is supported.
Eco-Friendly Option
With digital receipts and reduced paper usage, contactless transactions contribute to sustainability efforts. They also reduce the need for plastic cards as mobile payments become more popular.
Challenges and Limitations
Device Compatibility
Not all smartphones or POS terminals support NFC. Adoption is still growing, especially in some developing regions.
Technical Glitches
Sometimes transactions fail due to poor signal, low battery on your phone, or misalignment between device and terminal.
Fraud Concerns
Though rare, fraud is still a concern. Lost or stolen devices can potentially be used for unauthorized transactions—though spending limits and security features help mitigate this.
Privacy Concerns
Some users worry about how their data is stored and shared. Understanding the privacy policies of mobile wallet providers is essential for informed usage.
Real-World Applications
Public Transit
Cities like London, New York, and Tokyo allow passengers to tap and go using their contactless cards or mobile wallets on buses and subways.
Retail and Hospitality
From big chains to local boutiques, many retailers now support contactless payments. Restaurants use them to speed up checkout, and cafes find them particularly useful for busy morning rushes.
Events and Venues
Concerts, sports arenas, and festivals have adopted contactless payments to reduce lines and increase security. Some events are entirely cashless now.
Parking and Toll Roads
Contactless payments are now used in parking garages, meters, and toll systems, offering a faster way to navigate cities.
Healthcare and Pharmacies
Many pharmacies and clinics now support contactless payments, reducing handling of cards and cash and speeding up transactions in often time-sensitive environments.
Educational Institutions
Universities and schools are integrating contactless systems in cafeterias, bookstores, and libraries, improving access and accountability.
Mobile Wallets: A Closer Look
Apple Pay
Uses biometric authentication (Face ID or Touch ID) and works across Apple devices. Includes built-in privacy protections.
Google Pay
Supports a wide range of Android devices and integrates with other Google services like Gmail for receipts.
Samsung Pay
In addition to NFC, it uses Magnetic Secure Transmission (MST), allowing it to work with older magnetic stripe terminals.
Regional Wallets
In some regions, wallets like Alipay, Paytm, and M-Pesa are dominating the contactless landscape, tailored to local financial systems and regulations.
Setting Up Contactless Payments
For Users:
- Check Compatibility: Make sure your card or phone supports contactless payments.
- Enable NFC: Turn on the NFC function in your phone settings.
- Add Your Card: Use your mobile wallet app to add your credit/debit card.
- Authenticate: Most wallets require biometrics or a passcode.
- Start Tapping: You’re good to go!
For Merchants:
- Upgrade POS Terminal: Ensure it supports NFC.
- Train Staff: Make sure employees know how to process contactless payments.
- Promote the Option: Let customers know they can tap to pay.
- Integrate Loyalty Programs: Link loyalty points or discounts to contactless transactions to encourage repeat business.
The Future of Contactless Payments
Biometric Verification
Soon, fingerprint or facial recognition may become the default method of verifying payments—even with physical cards.
Increased Spending Limits
As adoption grows and fraud remains low, banks may continue to increase limits on contactless payments.
Integration with IoT Devices
Smart refrigerators, cars, and even vending machines could come equipped with payment capabilities.
Global Adoption
Countries that were slow to adopt NFC are now catching up, especially after the pandemic highlighted the value of contactless options.
Cryptocurrency Integration
Some fintech startups are exploring the integration of crypto wallets with contactless payment systems, bringing decentralized finance into everyday transactions.
AI and Predictive Technology
Artificial intelligence will likely play a bigger role in personalizing payment experiences, suggesting payment methods based on time, location, and previous habits.
Final Thoughts: More Than Just a Tap
Contactless payments are more than a trendy convenience—they represent a fundamental shift in how we interact with money. As the technology matures, we can expect even faster, safer, and more personalized experiences.
By understanding how the system works and how to use it securely, you not only stay ahead of the curve—you become part of the transformation. From tapping your card at a local coffee shop to paying for a subway ride in Tokyo, the future of commerce is contactless, and it’s already here.
So the next time you hear that familiar beep at the checkout, remember: you’re not just buying a latte. You’re participating in one of the most seamless technological evolutions of our time—and you’re doing it with just a tap.