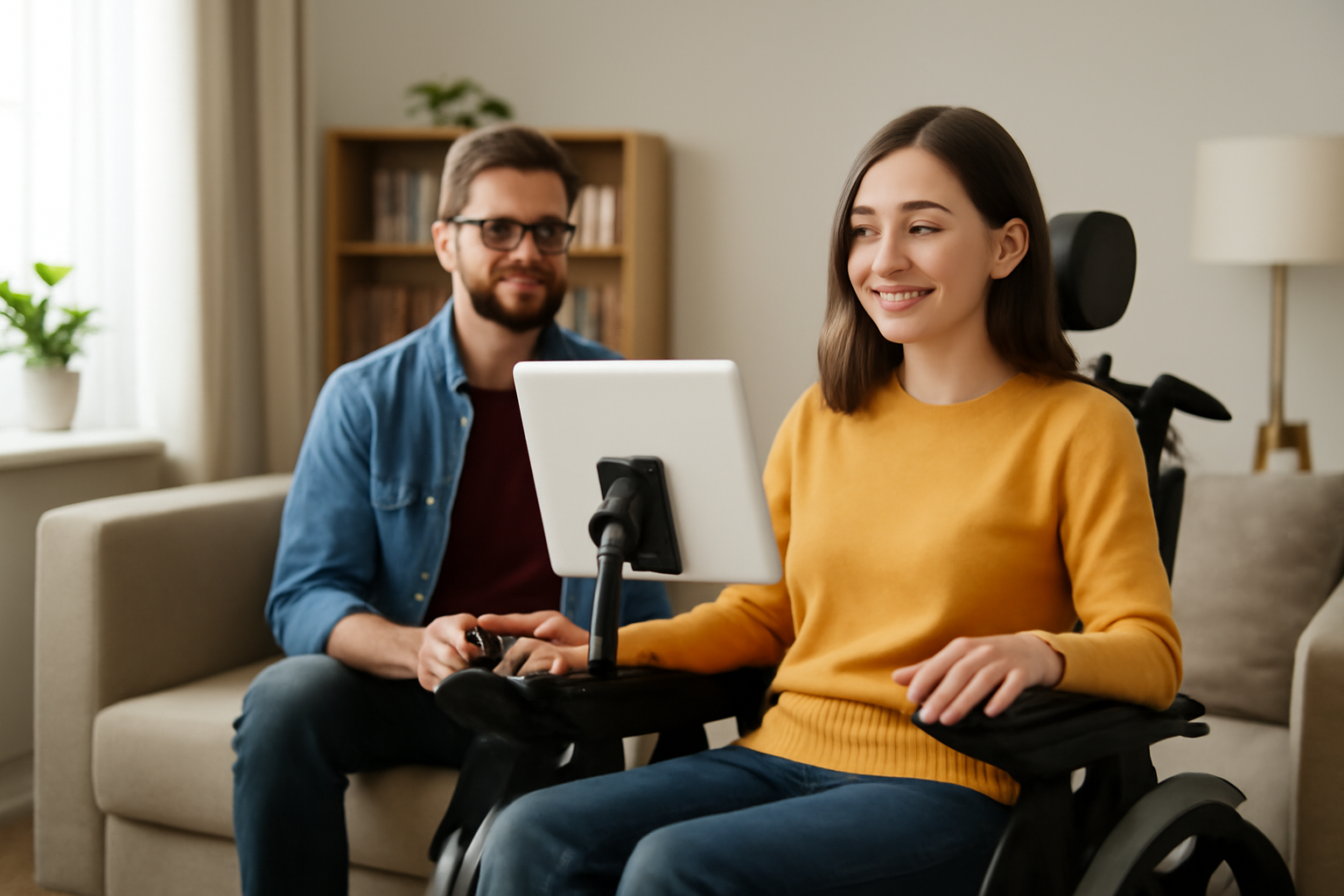
In recent years, technology has made significant strides in breaking down barriers and creating a more inclusive world. For people with disabilities, innovations in accessible technologies have transformed the way they interact with the world around them. Whether it’s through mobility aids, communication devices, or digital tools, these technologies are helping people live more independent, fulfilling lives.
In this article, we will explore some of the most impactful accessible technologies available today, the challenges they address, and how they make life easier for individuals with various disabilities.
1. Mobility Assistance Technologies
Smart Wheelchairs and Mobility Aids
One of the most crucial areas where technology has made significant advancements is in mobility aids. Wheelchairs, for example, have evolved tremendously over the years, thanks to innovations in smart technology. Today, powered wheelchairs equipped with sensors, motorized control systems, and even AI-driven navigation are transforming the lives of people with limited mobility.
Smart wheelchairs can navigate through different terrains with ease and can even adjust the seating position for comfort. Some advanced models are controlled via mobile apps, making it easier for users to customize settings like speed, tilt, and direction. This enhances independence, as users no longer rely on others for basic adjustments or transportation.
Additionally, some smart wheelchair models now come with built-in safety features, such as automatic collision detection, which prevents users from running into obstacles. This functionality is particularly important for people who have limited visibility or spatial awareness, providing an extra layer of protection.
Exoskeletons: Empowering Mobility
Another breakthrough in mobility technology is the development of exoskeletons. These wearable robotic suits can assist individuals with spinal cord injuries or paralysis to regain the ability to stand, walk, or even climb stairs. While still relatively expensive and in the early stages of widespread adoption, exoskeletons offer an incredible sense of freedom and empowerment, giving users the chance to experience mobility again.
Exoskeletons work by using motors and sensors to mimic natural human movement. For example, the ReWalk exoskeleton allows individuals to walk upright using a series of motors that move the legs in a similar pattern to natural walking. As research and development in this field continue to advance, we can expect exoskeletons to become more affordable and accessible, potentially changing the lives of millions of people living with mobility impairments.
2. Assistive Communication Tools
Speech-to-Text Technology
For people with hearing or speech impairments, communication can be a significant challenge. Speech-to-text technology has revolutionized the way individuals with disabilities can interact with others, participate in conversations, and perform tasks that require verbal communication.
Popular applications like Google Live Transcribe or Otter.ai provide real-time transcription, allowing people who are deaf or hard of hearing to read spoken words on their devices. These tools use machine learning algorithms to accurately transcribe speech into text, enabling users to follow conversations, attend meetings, or even take notes with ease.
Moreover, these technologies have become more precise over time, with improvements in natural language processing (NLP) algorithms that can handle complex speech patterns, regional accents, and technical jargon. This makes them more reliable for a wide range of communication needs, from casual conversations to professional meetings.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices
For individuals who have difficulty speaking, AAC devices provide an essential tool for communication. These devices range from simple picture boards to advanced speech-generating devices (SGDs). SGDs allow users to type or select images that the device then vocalizes, helping people with speech disabilities express themselves more effectively.
One widely used AAC device is the Tobii Dynavox, which offers eye-tracking technology that allows users to control the device with their gaze, making it especially beneficial for individuals with limited physical mobility. These devices enhance social interaction, improve emotional well-being, and offer greater independence in everyday life.
Additionally, some SGDs now feature customizable options for personalization, such as voice preferences and language options, which ensure users feel a sense of ownership over their communication device. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect these devices to become even more sophisticated, offering seamless integration with other digital platforms and even advanced artificial intelligence capabilities.
3. Visual Impairment Assistance
Screen Readers
For people with visual impairments, screen readers are invaluable tools. Screen readers are software programs that convert digital text into synthesized speech, allowing users to navigate websites, read books, or interact with devices independently. Popular screen readers include JAWS (Job Access With Speech), NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access), and VoiceOver for Apple devices.
These technologies make digital content accessible to those who cannot see or have limited vision, ensuring they can engage with everything from social media to academic resources. In addition to reading text aloud, screen readers often provide navigational commands and audio cues that help users understand the structure of a webpage or document.
A new development in screen reader technology is the use of AI-powered context recognition, which can help users not only read text but also identify visual elements, such as images or graphics, on a webpage. For instance, AI can describe images, charts, or infographics to users in a way that is contextually meaningful, enhancing the overall browsing experience.
Smart Glasses
Smart glasses are another exciting technology designed to assist individuals with visual impairments. For instance, companies like Aira and eSight are developing smart glasses that use real-time image recognition to provide information about the environment around the user. These devices have cameras that capture images of the user’s surroundings and relay the information to a trained assistant or artificial intelligence system, offering users detailed descriptions of what they are looking at.
Smart glasses can help with activities such as reading street signs, identifying objects, and even recognizing faces, all of which greatly enhance the user’s ability to navigate the world independently. By pairing these glasses with other assistive technologies, such as GPS or voice-activated assistants, individuals with visual impairments can experience a greater sense of autonomy and confidence in daily activities.
4. Hearing Impairment Assistance
Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implants
For individuals with hearing impairments, hearing aids and cochlear implants have been groundbreaking technologies that significantly improve quality of life. Hearing aids amplify sound to make it easier for individuals with hearing loss to participate in conversations and enjoy activities like watching television or listening to music.
Cochlear implants, on the other hand, are surgically implanted devices that provide a sense of sound to individuals with severe hearing loss. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sound, cochlear implants directly stimulate the auditory nerve, enabling users to perceive sound more naturally. Both of these technologies have helped millions of people hear better and engage more fully in their social and professional lives.
A new trend in hearing technology is the integration of hearing aids with smartphones, allowing users to adjust their devices remotely and even customize sound profiles based on their environment. This level of personalization enables individuals with hearing impairments to have a more tailored auditory experience, enhancing their overall hearing and communication abilities.
Real-Time Captioning and Sign Language Recognition
Real-time captioning systems and sign language recognition technologies are also making a huge difference in communication for people with hearing impairments. Real-time captioning involves displaying captions of spoken words during live events, meetings, or conversations. Services like Zoom and Google Meet now include real-time captioning features that help participants with hearing loss follow along during virtual meetings.
Moreover, advancements in sign language recognition technology have resulted in apps and devices that can translate sign language into text or speech. This allows individuals who use sign language to communicate more easily with those who do not understand it, bridging a crucial communication gap.
In particular, some apps now combine machine learning with sign language recognition, enabling more accurate translation of gestures and signs. As this technology improves, it could lead to the development of seamless communication tools that allow for a more fluid exchange of ideas between people with and without hearing impairments.
5. Cognitive and Learning Disabilities
Cognitive Assistive Technology
People with cognitive disabilities, such as those with autism or Alzheimer’s disease, often require specialized tools to help them navigate everyday tasks. Cognitive assistive technologies include applications that help with organization, memory, and task management.
For example, apps like “Todoist” or “Evernote” can help individuals create reminders, organize their day, and break tasks into smaller, manageable steps. These apps provide visual and auditory cues, making them easy to use for people with different cognitive abilities. For individuals with Alzheimer’s, technologies like GPS-enabled trackers and medication reminders can help them maintain independence while ensuring their safety.
In the realm of autism, apps and digital platforms are being designed to help individuals develop social skills, practice emotional regulation, and improve communication. For example, apps like “The Social Express” provide interactive lessons that teach social behaviors through role-playing scenarios. These tools are designed to be engaging while offering a supportive learning environment.
Virtual Reality (VR) for Therapy
Virtual Reality (VR) is also being used to help people with cognitive disabilities, particularly in therapeutic settings. VR can simulate real-world scenarios that allow users to practice social interactions, problem-solving, or other cognitive tasks in a safe, controlled environment. This can be especially helpful for people on the autism spectrum, as VR offers a non-threatening way to practice communication and social skills.
Therapists are using VR to create simulations of social situations, such as going to a grocery store, interacting with strangers, or even handling stressful encounters. By practicing these situations in a virtual world, individuals can build confidence and improve their social competency in a low-pressure environment.
6. The Future of Accessible Technologies
While we have made incredible progress in accessible technology, the journey is far from over. The future holds exciting possibilities for people with disabilities, with innovations like brain-computer interfaces, advanced AI tools, and more intuitive, responsive devices on the horizon.
As these technologies evolve, they will continue to enhance independence, improve quality of life, and provide people with disabilities the freedom to live life on their terms. As society becomes more aware of the needs of disabled individuals, we can expect an even greater push for inclusive design, making accessibility a standard feature in all technologies.
Technological advancements such as AI-driven prosthetics, which can adapt to user needs in real-time, and voice-activated assistants that seamlessly integrate with everyday devices, are paving the way for a future where disability is less of a limitation. The integration of accessible features into consumer devices, such as smartphones and home assistants, also plays a vital role in making these technologies more mainstream and available to a wider audience.
Conclusion
Accessible technologies have already changed the lives of millions of people with disabilities, and they will continue to play a vital role in shaping a more inclusive world. From mobility aids and communication tools to assistive devices for those with visual, hearing, or cognitive impairments, these innovations not only improve quality of life but also promote independence and participation in society.
As these technologies advance, they hold the promise of further empowering individuals with disabilities, enabling them to lead fulfilling, autonomous lives. The future of accessible technology is bright, and it is an exciting time to witness how these advancements will continue to break down barriers and open up new possibilities for all.