Cultural heritage plays a crucial role in defining the identity, history, and values of societies. It encompasses monuments, traditions, languages, customs, music, and art that have been passed down from one generation to the next. Preserving this heritage ensures that future generations can understand their roots, appreciate the achievements of their ancestors, and learn from the past. However, as the world becomes increasingly modernized, the preservation of cultural heritage faces numerous challenges, such as natural disasters, urbanization, and the passage of time.
In recent years, technology has emerged as a powerful ally in the effort to safeguard cultural heritage. From digital archives to 3D scanning and virtual reality (VR), technological advancements are providing new ways to protect, restore, and promote cultural treasures. In this article, we will explore how technology is transforming the preservation of cultural heritage and why it is becoming an essential tool for cultural conservation efforts worldwide.
The Challenges of Cultural Heritage Preservation
Before delving into how technology is helping preserve cultural heritage, it is important to understand the challenges faced in this field. The preservation of cultural assets is often threatened by various factors:
1. Environmental Factors
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes can cause severe damage to historical buildings, monuments, and artifacts. Climate change is also exacerbating the deterioration of cultural heritage sites, as rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and increased humidity impact the physical condition of these sites.
2. Urbanization and Development
As cities grow and develop, there is often a conflict between modern construction and the preservation of historical sites. Buildings and monuments that are hundreds of years old may be demolished or altered to make way for new infrastructure, resulting in the loss of invaluable cultural heritage.
3. Aging and Physical Degradation
Over time, the materials used to construct historical sites or artifacts can degrade due to age, wear and tear, and environmental exposure. Many cultural objects, such as manuscripts, paintings, and textiles, are fragile and susceptible to deterioration from light, humidity, and handling.
Given these challenges, new methods are needed to preserve cultural heritage for future generations. Technology has become an invaluable tool in addressing these issues, allowing for more efficient, accurate, and long-lasting preservation techniques.
1. Digital Documentation and Archiving
One of the most significant ways in which technology is helping preserve cultural heritage is through digital documentation and archiving. By creating high-resolution digital records of artifacts, buildings, and sites, researchers and conservators can ensure that even if physical objects are damaged or lost, there will still be accurate records of them for future study and reference.
1.1 3D Scanning and Modeling
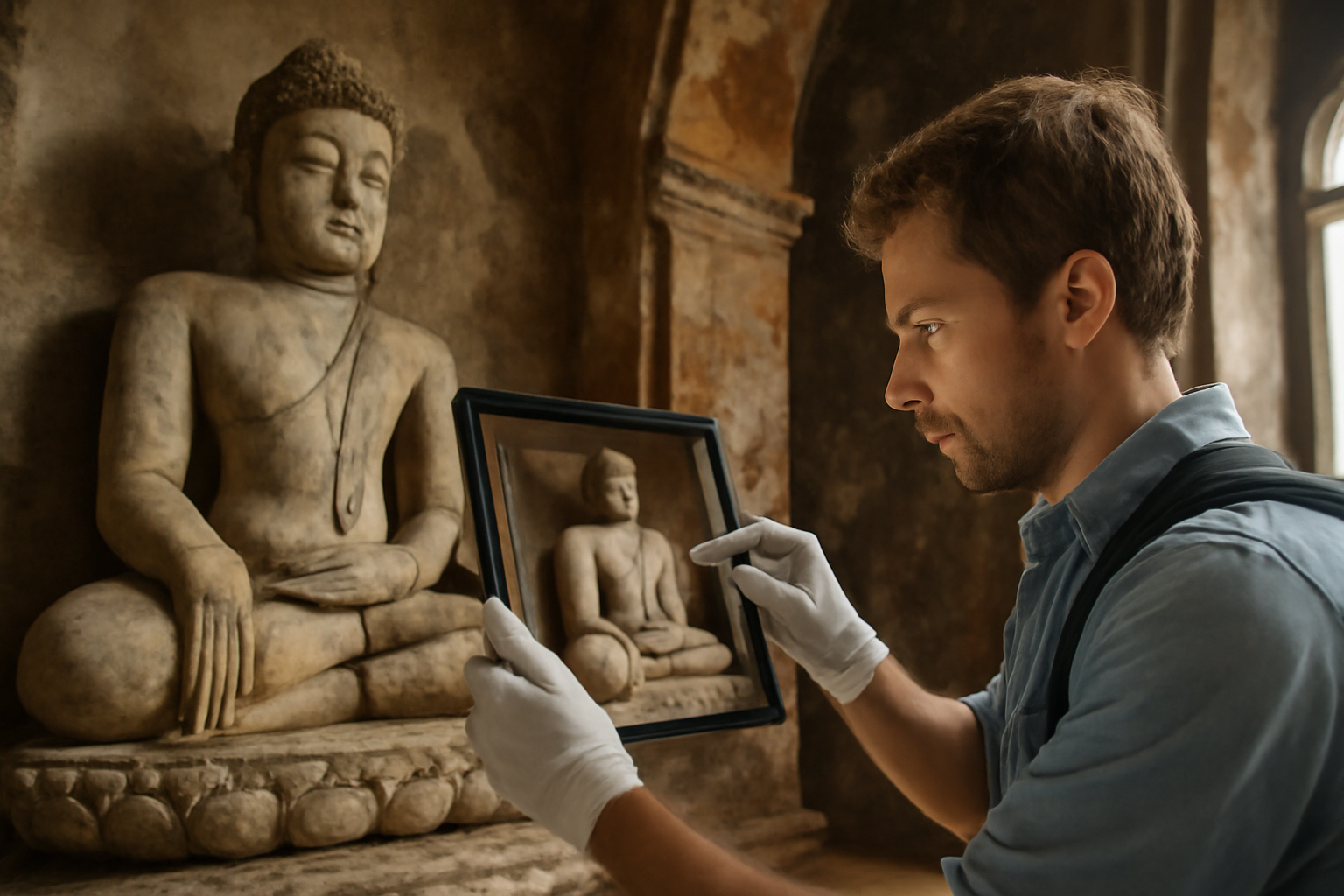
One of the most revolutionary technological advancements in cultural heritage preservation is the use of 3D scanning and modeling. This technology allows for the creation of highly detailed digital replicas of objects, monuments, and even entire historical sites. Using laser scanners and photogrammetry techniques, conservators can capture every minute detail of a structure or artifact, from textures to dimensions, with incredible precision.
Example: The Altamira Cave in Spain, home to prehistoric paintings, was digitally scanned using 3D modeling technology to create a replica of the cave. This replica allows visitors to experience the cave without physically entering it, which helps protect the original from the potential damage caused by human interaction and environmental factors.
Why It’s Essential:
- Non-Invasive: 3D scanning is a non-invasive process, which means that the cultural heritage object or site is not physically altered or damaged during the recording process.
- Preservation of Details: Digital records preserve the fine details of artifacts, such as intricate carvings or paintings, which might otherwise degrade over time.
- Accessibility: Digital archives make it possible for scholars, researchers, and the general public to access and study cultural heritage from anywhere in the world.
1.2 Digital Archiving and Virtual Libraries
In addition to 3D scanning, digital archiving allows for the preservation of texts, photographs, manuscripts, and other written materials. By converting historical documents into digital formats, libraries and museums can safeguard rare books, manuscripts, and records from the risks of deterioration.
Example: The Digital Public Library of America (DPLA) hosts millions of digitized photographs, documents, and texts from cultural institutions across the United States. This initiative allows anyone to access these valuable historical resources online, ensuring that they are preserved and accessible for future generations.
Why It’s Essential:
- Long-Term Preservation: Digital archives ensure that cultural heritage is not lost due to the physical degradation of materials.
- Global Access: Digitizing cultural artifacts makes them accessible to a global audience, promoting education and fostering a greater understanding of cultural history.
2. Restoration through Artificial Intelligence
AI is playing an increasingly important role in the restoration of cultural heritage. By analyzing historical data and studying the physical characteristics of damaged artifacts, AI can assist in the reconstruction and restoration of objects that have been damaged over time. AI-powered tools can identify patterns, recommend restoration methods, and even predict the most likely appearance of an object based on available data.
2.1 AI for Image and Video Restoration
AI has been particularly useful in restoring old images, films, and photographs that have been damaged by age or environmental factors. Through machine learning algorithms, AI systems can repair damaged parts of images, enhance resolution, and even colorize black-and-white photographs.
Example: The AI-powered software used by the British Film Institute (BFI) has been able to restore and colorize old films from the early 20th century, providing a more vivid and accurate representation of historical events for modern audiences.
Why It’s Essential:
- Efficiency: AI speeds up the restoration process, allowing for the efficient recovery of damaged materials without the need for manual restoration.
- Accuracy: AI tools can analyze and repair damaged images with high precision, often surpassing the capabilities of human restorers.
2.2 AI in Archaeological Research
AI is also playing a role in archaeology, where it helps researchers analyze historical data and predict the location of artifacts or ruins. AI algorithms can sift through large amounts of data from excavation sites, satellite imagery, and historical records to uncover hidden patterns and relationships that may lead to the discovery of new heritage sites.
Example: AI-powered tools have been used in Egypt to analyze satellite images and uncover previously unknown pyramids and burial sites, aiding archaeologists in their search for new cultural treasures.
Why It’s Essential:
- Enhanced Discoveries: AI can uncover patterns and hidden information that might have been missed by human researchers, leading to new discoveries.
- Preserving the Past: By predicting the locations of historical sites, AI helps direct preservation efforts to areas that may be at risk of damage.
3. Virtual and Augmented Reality
Another way that technology is helping preserve cultural heritage is through the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). These immersive technologies allow individuals to experience cultural sites and artifacts in a way that feels real, while also providing a safe and sustainable way to interact with these treasures.
3.1 Virtual Reality for Virtual Tours
Virtual reality is being used to create virtual tours of cultural heritage sites, allowing users to explore ancient ruins, historical landmarks, and museums from the comfort of their homes. These tours are especially valuable for locations that are difficult to access or at risk of damage due to over-tourism.
Example: The Palmyra ruins in Syria, which were severely damaged during the Syrian Civil War, have been digitally recreated using VR technology. Visitors can now experience these historic sites in their full splendor without physically visiting the location.
Why It’s Essential:
- Preservation through Virtual Access: VR allows for the preservation of cultural heritage sites by reducing the physical foot traffic that can contribute to degradation.
- Engaging Learning Experience: Virtual tours make learning about cultural history more engaging and accessible for people of all ages and backgrounds.
3.2 Augmented Reality for Interactive Experiences
Augmented reality enhances the real world by overlaying digital content on physical objects. In cultural heritage preservation, AR is being used to provide interactive, educational experiences at museums and historical sites. Visitors can use AR devices to learn more about an artifact’s history, watch videos, or interact with digital reconstructions of lost or damaged items.
Example: The Louvre Museum in Paris has incorporated AR into its exhibits, allowing visitors to use AR-enabled devices to interact with 3D representations of ancient Egyptian artifacts, providing a deeper understanding of the objects and their context.
Why It’s Essential:
- Interactive Learning: AR makes learning about cultural heritage more interactive, allowing visitors to engage with exhibits in a hands-on way.
- Bringing History to Life: AR helps bring historical objects to life by providing additional context, visuals, and interactive features.
4. Blockchain for Provenance and Ownership
Blockchain technology, known for its use in cryptocurrency, is also being used to track the provenance and ownership of cultural heritage items. Blockchain’s decentralized ledger system ensures that the history of an object—whether it’s an artwork, manuscript, or artifact—can be traced back to its origin, helping to prevent theft and illegal trade.
Example: The use of blockchain technology is being explored to protect the ownership of art and antiquities, ensuring that these items are not stolen and that their historical significance is preserved.
Why It’s Essential:
- Preventing Theft and Loss: Blockchain ensures that the ownership of cultural heritage items is transparent, reducing the risk of illegal trade and looting.
- Secure Provenance: Blockchain provides an immutable record of an item’s provenance, which is crucial for verifying its authenticity and historical value.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, it plays an increasingly vital role in the preservation of cultural heritage. From digital archiving and 3D scanning to AI-powered restoration and virtual reality tours, technology is enabling us to safeguard and share cultural treasures in ways that were once unimaginable. These innovations not only help protect the past but also ensure that future generations can engage with and learn from their cultural heritage.
With the continued growth of these technologies, we can expect even greater strides in the preservation of cultural heritage, ensuring that the stories, knowledge, and artistry of our ancestors are not lost to time.