Introduction: The Power of Layer by Layer
What was once science fiction is now commonplace—3D printers are no longer confined to industrial labs or research institutions. These devices, which build objects layer by layer using digital models, have evolved into powerful tools with real-world applications that touch our daily lives in unexpected ways.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a hobbyist, or simply curious about the future, this article explores how 3D printing is reshaping industries, revolutionizing creativity, and offering practical solutions to everyday problems. Beyond the buzzwords, we’ll look at real examples, practical uses, and the surprising places you’ll find this innovative technology making a difference.
What Is 3D Printing and How Does It Work?
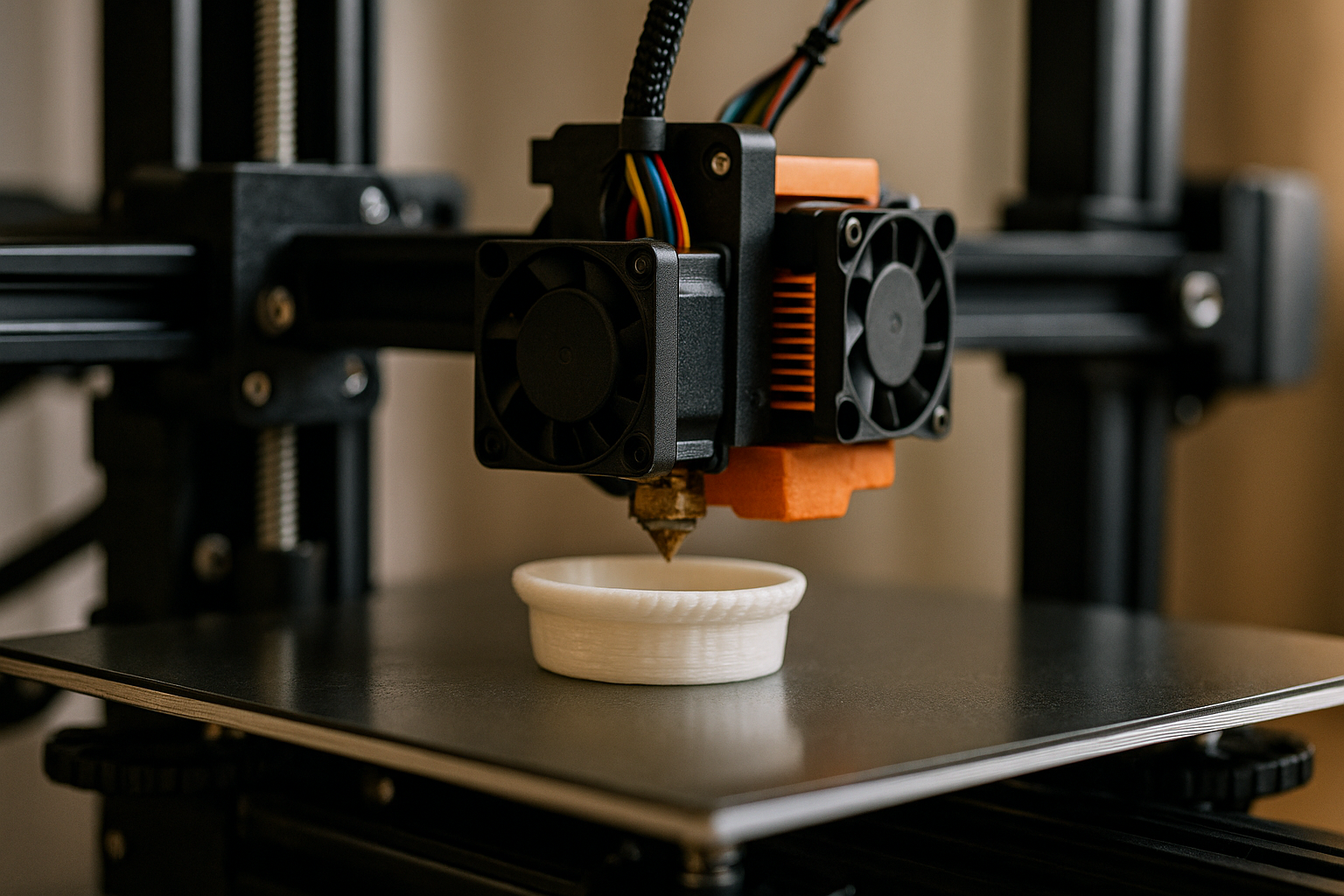
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Instead of subtracting material as in traditional manufacturing, 3D printers add material layer by layer until the final object is complete.
Key Components:
- Design File: Created using CAD (computer-aided design) software or scanned from a real object.
- Printer: Machines that follow the design instructions and deposit materials precisely.
- Material: Typically plastic (PLA, ABS), resin, metal, or even food and biological matter.
Process Overview:
- Design the object digitally.
- Slice the design into layers using slicing software.
- Send the file to the printer.
- The printer adds material one layer at a time.
- Post-process the object (e.g., cleaning, curing, or polishing).
Home and Personal Use: DIY and Beyond
Custom Household Items
Have a broken drawer handle? A light switch cover that doesn’t exist in stores? With a 3D printer, you can design and produce custom parts to fix or upgrade everyday household items. This democratizes repair and promotes sustainability by extending the life of objects.
Toys and Games
Parents and hobbyists alike are using 3D printers to create custom toys, puzzles, board game pieces, and figurines. The ability to personalize design and color adds a layer of creativity and personalization.
Educational Tools
3D printers are finding their way into classrooms and home schools:
- Anatomy models
- Historical artifacts
- Math and geometry tools
They make abstract concepts tangible and interactive, enhancing student engagement. Additionally, teachers can use 3D printers to create custom learning aids suited to their unique curriculum, enabling more inclusive and adaptable learning environments.
Fashion and Accessories
From jewelry to wearable gadgets, 3D printing allows users to prototype and produce unique accessories that are hard to find or expensive to purchase. Artists and designers use it for experimentation and limited editions. Consumers benefit from on-demand creation, reducing reliance on mass production and minimizing waste.
Health and Medical Applications
Prosthetics and Orthotics
3D printers are revolutionizing the production of prosthetic limbs. Custom-fit, lightweight, and cost-effective prosthetics can now be designed and printed locally—even in underserved communities. The process allows for rapid iteration and personalization based on a user’s needs. In developing countries, organizations are using 3D printers to restore mobility and confidence to individuals who might not otherwise have access to such life-changing technology.
Dental and Orthodontic Tools
Dentists use 3D printing to create precise models of teeth, retainers, crowns, and aligners. These products fit better, reduce patient discomfort, and shorten production timelines. Clinics can now deliver same-day restorations, improving both efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Surgical Planning and Implants
Doctors use printed anatomical models for surgical simulations. Custom implants, such as cranial plates or jawbones, can also be printed based on a patient’s exact anatomy, reducing complications and improving outcomes. Surgeons report greater confidence and accuracy when operating on complex cases with the help of pre-surgical models.
Bioprinting (Emerging)
While still in its infancy, bioprinting aims to print human tissue—skin, cartilage, and eventually, organs. Though not yet widespread, early developments show promise for regenerative medicine. Researchers are working toward fully functional organ printing, which could eventually address transplant shortages and ethical concerns associated with organ donation.
Food Printing: Eating Innovation
3D food printers use ingredients like chocolate, dough, and purees to create intricate edible designs. Applications include:
- Decorative cake toppers
- Nutritionally tailored meals for the elderly
- Food art for restaurants and events
Chefs are using 3D printers to push culinary boundaries and personalize dining experiences. In some hospitals and care facilities, food printers are being explored as a way to prepare appealing, easy-to-swallow meals for patients with dietary restrictions or dysphagia.
Automotive and Aerospace
Rapid Prototyping
Automakers and aerospace engineers use 3D printing to quickly produce and test parts before mass production. This reduces time-to-market and allows for iterative improvements. Engineers can test multiple design versions in days instead of months, significantly accelerating the innovation process.
Replacement Parts
For vintage cars or specialized aircraft, sourcing spare parts can be difficult. 3D printing offers a solution by replicating hard-to-find components on-demand. Custom tools and jigs can also be created to assist with repairs, enhancing efficiency in maintenance operations.
Lightweight Components
Printing complex, lightweight structures helps reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency, especially in aerospace applications. Companies like Airbus and Boeing are already flying aircraft with 3D-printed components onboard, citing weight savings as a major advantage.
Architecture and Construction
Scale Models
Architects use 3D printing to produce detailed scale models of buildings and landscapes. These models are useful for client presentations and design evaluations. Clients can better visualize the final outcome, and stakeholders can provide earlier feedback during the design process.
Full-Scale Buildings (Emerging)
Several companies are experimenting with printing entire homes and structures using large-scale printers and concrete-like materials. The benefits?
- Reduced labor costs
- Faster construction
- Less material waste
In some regions, 3D-printed homes are being explored as a solution to housing shortages. In places affected by natural disasters, rapid 3D construction offers hope for quick recovery and safe shelter.
Art and Creativity
Sculpture and Installations
Artists use 3D printing to bring intricate digital sculptures to life. The technology allows for geometric complexity and detail that would be nearly impossible with traditional techniques. This opens the door to new artistic expressions and hybrid forms of digital and physical creativity.
Music Instruments
Musicians and makers are experimenting with 3D-printed instruments like violins, flutes, and guitars—combining function with artistic design. These instruments can be customized for tonal quality, ergonomics, and visual aesthetics.
Animation and Props
Filmmakers and animators use 3D printers to create props, character models, and costume elements. This speeds up production and adds a tactile dimension to creative projects. Studios benefit from on-demand production and reduced outsourcing costs.
Industrial and Manufacturing Uses
Jigs, Fixtures, and Tooling
Factories are using 3D printers to create custom tools that improve production line efficiency. These items are often low-cost and designed for specific tasks. Because they can be produced internally, companies save time and resources while improving workflow.
Spare Parts and Inventory Management
Instead of holding vast inventories, businesses can store digital files and print parts on demand—saving space and reducing overhead. This just-in-time model streamlines supply chains and reduces waste.
Low-Volume Manufacturing
For specialized products or limited editions, 3D printing is ideal. It eliminates the need for expensive molds and reduces startup costs. Entrepreneurs and small businesses can now prototype and produce market-ready items at a fraction of traditional costs.
Emergency and Crisis Situations
Medical Supplies in Shortages
During crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, 3D printers were used to produce face shields, ventilator parts, and testing swabs. This decentralized production helped fill gaps in supply chains. Hospitals partnered with local makers to meet urgent needs.
Disaster Relief
In disaster-struck areas, 3D printing can be deployed to produce temporary shelters, water filters, and tools—quickly and cost-effectively. NGOs are exploring the use of portable 3D printers to assist communities in rebuilding infrastructure and restoring basic services.
Environmental and Sustainability Efforts
Reducing Waste
Additive manufacturing generates less waste than subtractive methods (like machining). This makes it more eco-friendly. By only using the material needed for each object, 3D printing significantly reduces scraps and byproducts.
Recycled Materials
Some 3D printers use recycled plastics or biodegradable materials. Researchers are exploring circular models where waste is transformed into printable filament. Closed-loop systems could be key to minimizing the environmental footprint of consumer goods.
Localized Production
Producing goods locally reduces carbon footprints related to transportation and distribution. This model also supports local economies and increases resilience in the face of global supply chain disruptions.
Future of 3D Printing
Multimaterial Printing
Printers that can handle multiple materials (e.g., plastic and metal or conductive and insulating) will open doors to more complex and integrated designs. Hybrid devices with embedded electronics, sensors, and mechanical parts are already being prototyped.
Smart Printing
AI and machine learning are being used to optimize printing parameters in real-time, improving quality and reliability. Predictive maintenance and automatic calibration features are making printers more efficient and accessible.
Accessibility and Cost Reduction
As prices drop and usability improves, more consumers, schools, and small businesses will adopt the technology. Simplified interfaces and open-source communities lower the barrier to entry for newcomers.
Regulation and Standards
As 3D printing becomes widespread, especially in healthcare and aerospace, regulatory frameworks will evolve to ensure safety and consistency. International standards will help guide best practices and boost confidence in printed products.
Practical Tips for Getting Started
- Choose the Right Printer: Entry-level printers like the Creality Ender or Prusa Mini are popular for beginners.
- Learn the Software: Familiarize yourself with CAD tools (e.g., TinkerCAD, Fusion 360) and slicers (e.g., Cura).
- Start Simple: Begin with basic designs and build your skills over time.
- Explore Communities: Join online forums like Reddit’s r/3Dprinting or Thingiverse to share designs and troubleshoot.
- Be Patient: Printing takes time and experimentation, but the results can be incredibly rewarding.
Final Thoughts: A Printer in Every Home?
3D printing is not just a niche hobby or industrial tool—it’s a transformative technology reshaping how we create, repair, learn, and innovate. Whether you’re designing custom jewelry, printing a spare part for your vacuum cleaner, or prototyping a new invention, 3D printers put the power of production in your hands.
As costs drop, materials diversify, and applications expand, it’s not far-fetched to imagine a future where having a 3D printer is as common as owning a microwave. And with the right mindset, anyone can harness this technology to solve problems, express creativity, and contribute to a more sustainable and personalized world.
From everyday fixes to life-changing innovations, the magic of 3D printing is all around us—layer by fascinating layer.